Virginia: Who Pays? 7th Edition

Virginia
Download PDF
All figures and charts show 2024 tax law in Virginia, presented at 2023 income levels. Senior taxpayers are excluded for reasons detailed in the methodology. Our analysis includes nearly all (98.8 percent) state and local tax revenue collected in Virginia. These figures depict Virginia’s standard deduction at its 2024 levels of $8,500 and $17,000. Those amounts are set to return to $3,000 and $6,000 over the next two years. As seen in Appendix E, this will increase the bottom fifth’s overall tax rate by 0.9 percentage points and cause the state to move 4 spots in the ITEP Inequality Index rankings, from 37th to 33rd most regressive.
State and local tax shares of family income
| Top 20% | |||||||
| Income Group | Lowest 20% | Second 20% | Middle 20% | Fourth 20% | Next 15% | Next 4% | Top 1% |
| Income Range | Less than $26,500 | $26,500 to $51,400 | $51,400 to $91,400 | $91,400 to $151,700 | $151,700 to $345,500 | $345,500 to $737,500 | Over $737,500 |
| Average Income in Group | $15,200 | $37,300 | $69,300 | $122,800 | $214,600 | $460,500 | $1,487,400 |
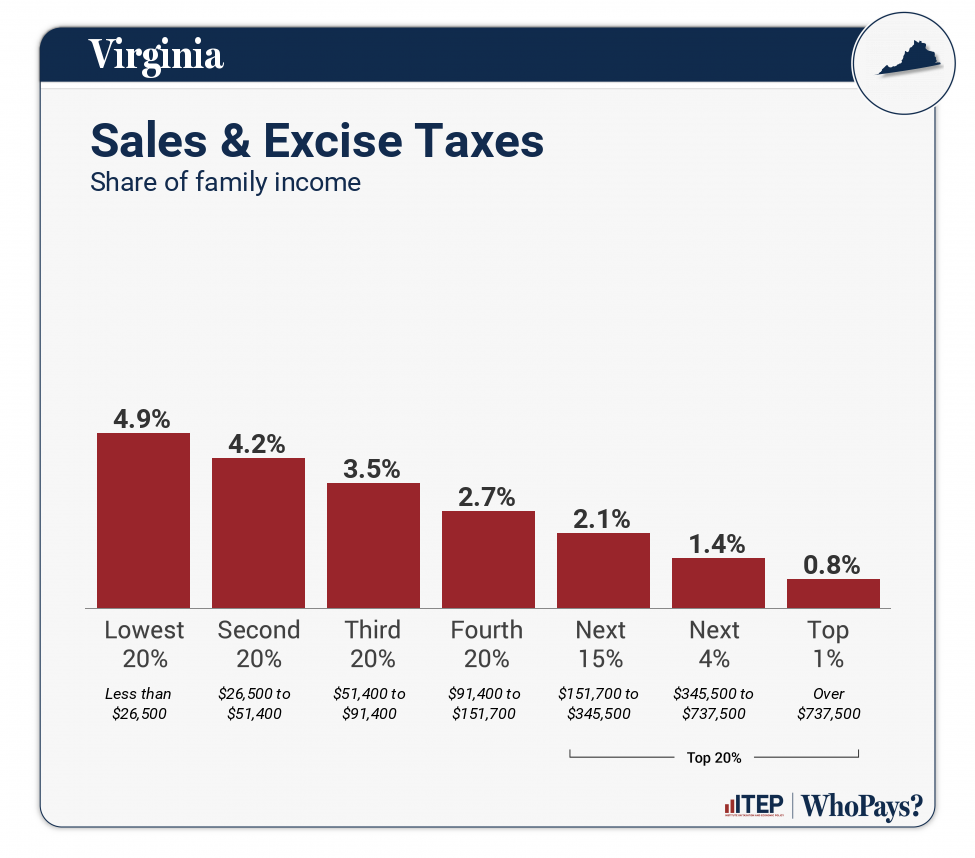
| Sales & Excise Taxes | 4.9% | 4.2% | 3.5% | 2.7% | 2.1% | 1.4% | 0.8% |
| General Sales–Individuals | 2.3% | 2.2% | 1.9% | 1.4% | 1.1% | 0.7% | 0.2% |
| Other Sales & Excise–Ind | 1.6% | 1.1% | 0.8% | 0.5% | 0.4% | 0.2% | 0.1% |
| Sales & Excise–Business | 1% | 1% | 0.9% | 0.7% | 0.6% | 0.5% | 0.5% |
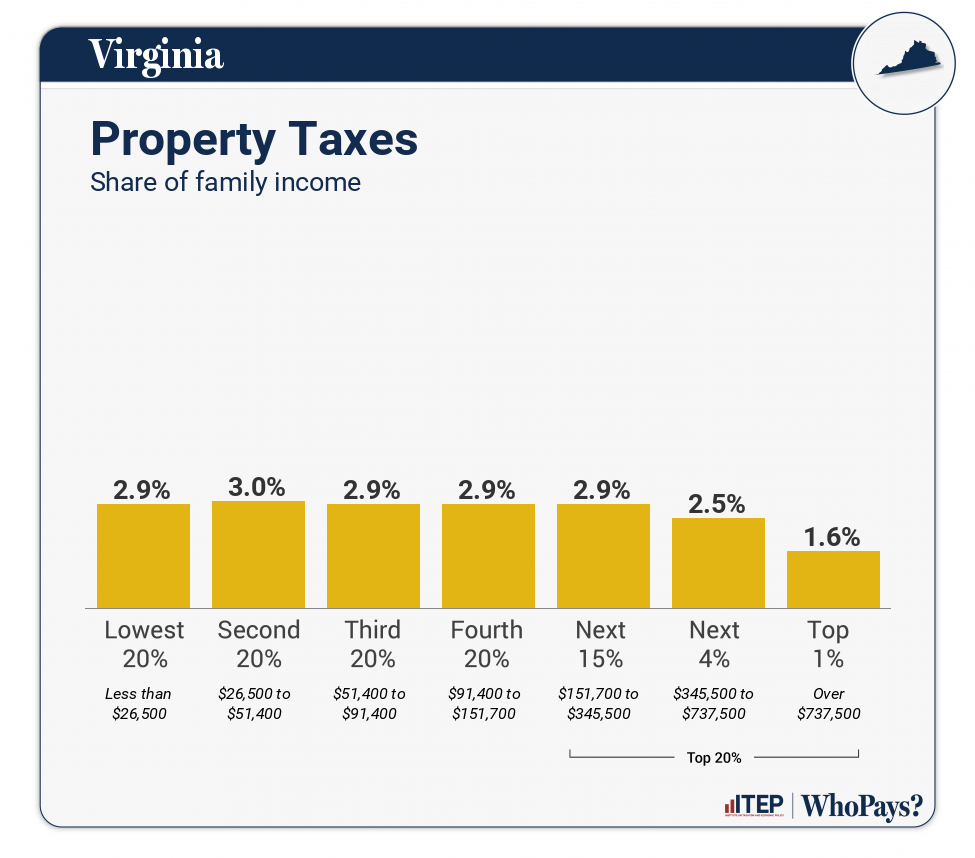
| Property Taxes | 2.9% | 3% | 2.9% | 2.9% | 2.9% | 2.5% | 1.6% |
| Home, Rent, Car–Individuals | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.4% | 1.9% | 0.7% |
| Other Property Taxes | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.6% | 1% |
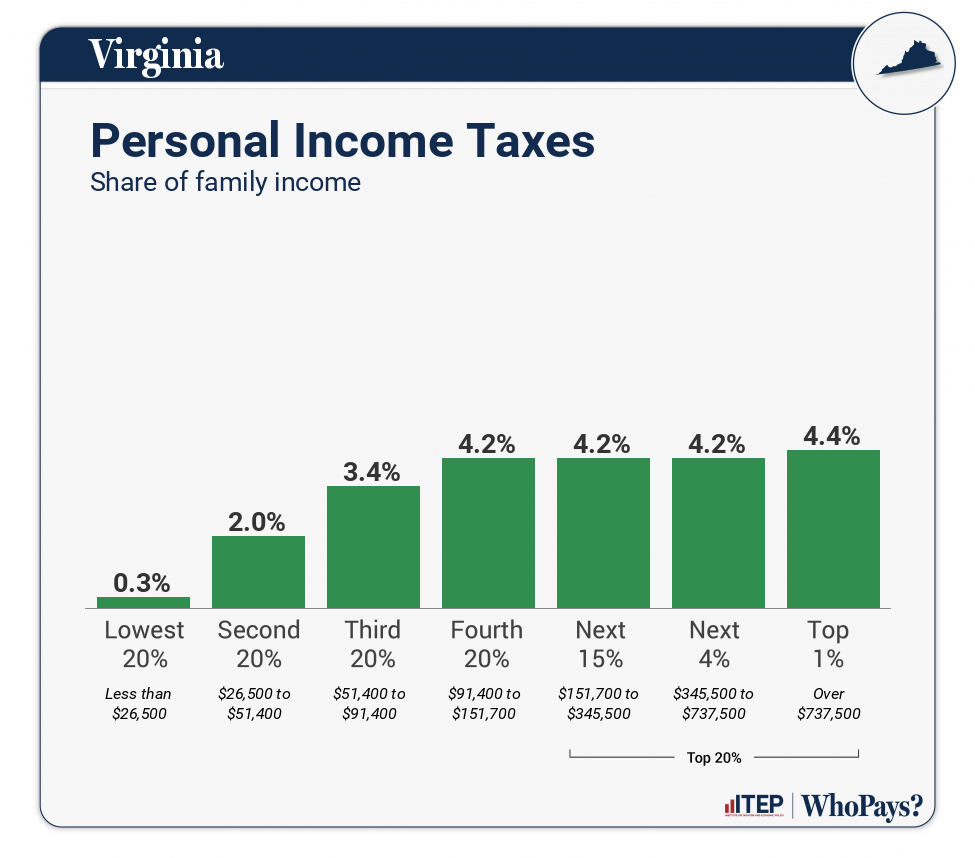
| Income Taxes | 0.4% | 2.1% | 3.5% | 4.3% | 4.2% | 4.3% | 4.5% |
| Personal Income Taxes | 0.3% | 2% | 3.4% | 4.2% | 4.2% | 4.2% | 4.4% |
| Corporate Income Taxes | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| Other Taxes | 0.5% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% |
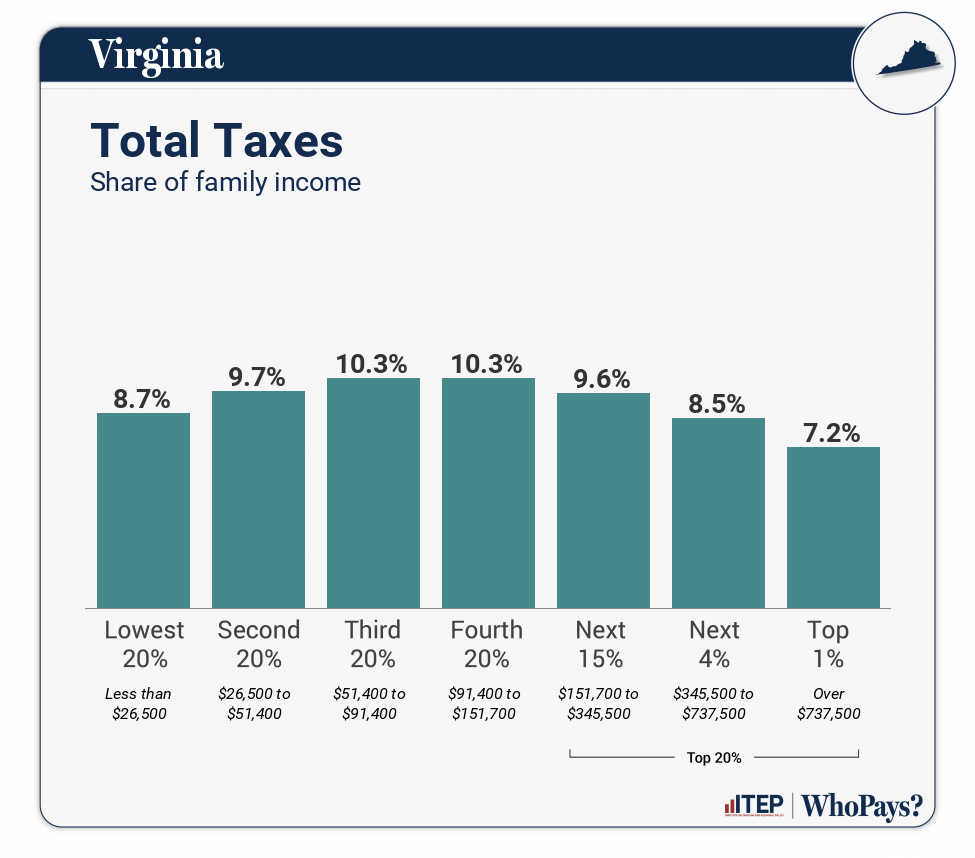
| TOTAL TAXES | 8.7% | 9.7% | 10.3% | 10.3% | 9.6% | 8.5% | 7.2% |
| Individual figures may not sum to totals due to rounding. | |||||||
ITEP Tax Inequality Index
Virginia has a hybrid system that is progressive through the bottom part of the income distribution and regressive through the top part. On balance, the overall system tilts regressive because high-income families pay the lowest overall tax rates. According to ITEP’s Tax Inequality Index, Virginia has the 37th most regressive state and local tax system in the country. Income disparities between high-income taxpayers and other families are larger in Virginia after state and local taxes are collected than before. (See Appendix B for state-by-state rankings and the report methodology for additional detail.)
Tax features driving the data in Virginia
|
Graduated personal income tax structure, though top rate kicks in at $17,000 so a large share of families face top rate
Refundable Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) (15 percent refundable; 20 percent nonrefundable)
|
|
|
No property tax “circuit breaker” credit for low-income, non-senior taxpayers
Narrow income tax brackets mean majority of taxpayers pay top income tax rate
Does not use combined reporting as part of its corporate income tax
Does not levy a tax on estates or inheritances
Local sales tax bases include groceries
No Child Tax Credit (CTC)
|